Maximizing Your Auditory Comfort
Achieving optimal auditory comfort is a significant aspect of overall well-being, particularly for individuals experiencing hearing challenges. Modern hearing aids offer sophisticated solutions designed to enhance the listening experience across various environments, thereby improving communication and engagement in daily life. Understanding the diverse options available, their functionalities, and how they are tailored to individual needs can empower users to make informed decisions that lead to greater auditory clarity and satisfaction.
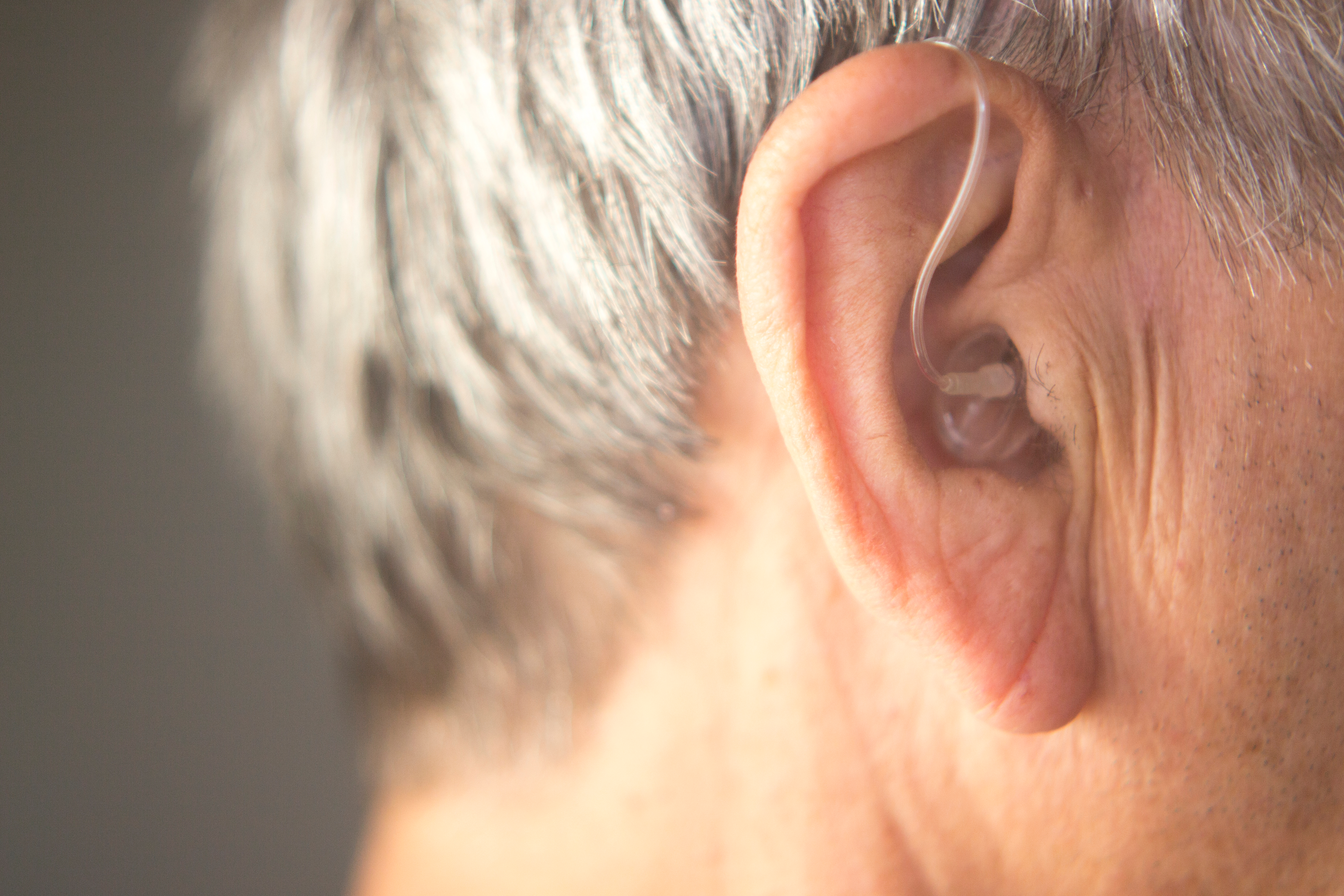
Hearing aids are intricate devices engineered to amplify sound and improve speech understanding for individuals with hearing loss. These devices have evolved considerably, offering a wide array of styles and technological features aimed at enhancing the user’s quality of life. Exploring the different types and how they function is a foundational step in identifying the most suitable solution for individual auditory requirements and lifestyle.
Understanding Hearing Aid Types: From Shape to Wearing Method
Hearing aids come in various forms, each designed to suit different degrees of hearing loss, aesthetic preferences, and comfort levels. The primary categories include Behind-The-Ear (BTE), Receiver-In-Canal (RIC), and In-The-Ear (ITE) styles. BTE aids sit behind the ear, with a tube connecting to a custom earmold or dome in the ear canal. RIC aids are similar to BTE but have the receiver (speaker) placed directly in the ear canal, connected by a thin wire, offering a more discreet profile. ITE aids are custom-made to fit entirely within the outer ear bowl, while smaller, more discreet versions like In-The-Canal (ITC) and Completely-In-Canal (CIC) fit partly or entirely within the ear canal, respectively. The choice often depends on the severity of hearing loss, manual dexterity, and cosmetic considerations.
Core Functions and Performance: Key Factors Determining the Listening Experience
The performance of hearing aids is determined by several core functions designed to process and deliver sound effectively. Digital signal processing is central to modern devices, allowing for precise amplification of specific frequencies while suppressing unwanted noise. Features such as noise reduction algorithms help to filter out background distractions, making conversations clearer in noisy environments. Directional microphones focus on sounds coming from the front, improving speech understanding. Connectivity options, including Bluetooth, allow direct streaming from smartphones and other devices, enhancing versatility. The overall listening experience is significantly influenced by how well these technologies work together to adapt to different soundscapes and personal hearing profiles.
Adaptation Testing and Scene Matching: Precisely Adapting to Hearing Needs
Effective use of hearing aids relies heavily on proper fitting and programming, a process known as adaptation testing or verification. This involves audiologists using specialized equipment, such as real-ear measurements, to ensure the hearing aid’s output matches the individual’s prescription and ear canal acoustics. Scene matching, or automatic environment detection, is a crucial feature in advanced hearing aids. These devices can analyze the surrounding sound environment—whether it’s a quiet room, a bustling restaurant, or an outdoor setting—and automatically adjust their settings to optimize sound clarity and comfort. This precise adaptation helps users navigate various listening situations with improved ease and understanding, minimizing the need for manual adjustments.
Budget and Cost-Effectiveness
The cost of hearing aids can vary widely, influenced by technology level, features, and the provider. Entry-level models typically offer basic amplification and noise reduction, while premium devices include advanced features like artificial intelligence, superior connectivity, and sophisticated environmental processing. It’s important to consider not only the upfront cost but also potential ongoing expenses such as batteries, maintenance, and follow-up appointments. Some insurance plans may offer partial coverage, and financing options are often available through providers.
| Product/Service | Provider | Cost Estimation (per device) |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Digital Hearing Aid | Online Retailers / Entry-level Clinics | $500 - $1,500 |
| Mid-Range Digital Hearing Aid | Independent Audiologists / Retail Chains | $1,500 - $3,000 |
| Premium Technology Hearing Aid | Independent Audiologists / Specialty Clinics | $3,000 - $6,000 |
| Over-the-Counter (OTC) Hearing Aids | Various Retailers (e.g., CVS, Best Buy) | $200 - $1,000 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Hearing Aid Usage Methods and Final Summary
Proper usage and care are essential for maximizing the lifespan and effectiveness of hearing aids. This includes regular cleaning, battery replacement or recharging, and protecting the devices from moisture and extreme temperatures. Many modern hearing aids can be controlled via smartphone apps, allowing users to adjust volume, switch programs, and even locate lost devices. Routine follow-up appointments with an audiologist are crucial for fine-tuning the devices as hearing needs may change over time. Understanding these usage methods ensures that individuals can consistently benefit from their hearing aids, maintaining optimal auditory comfort in their daily lives.
Selecting and adapting to hearing aids is a personalized journey that significantly impacts an individual’s connection to the world around them. By understanding the various types, core functionalities, the importance of precise fitting, and considering the financial aspects, individuals can make informed choices. Consistent use and proper maintenance further ensure that these devices provide sustained auditory comfort, fostering improved communication and an enhanced quality of life.




